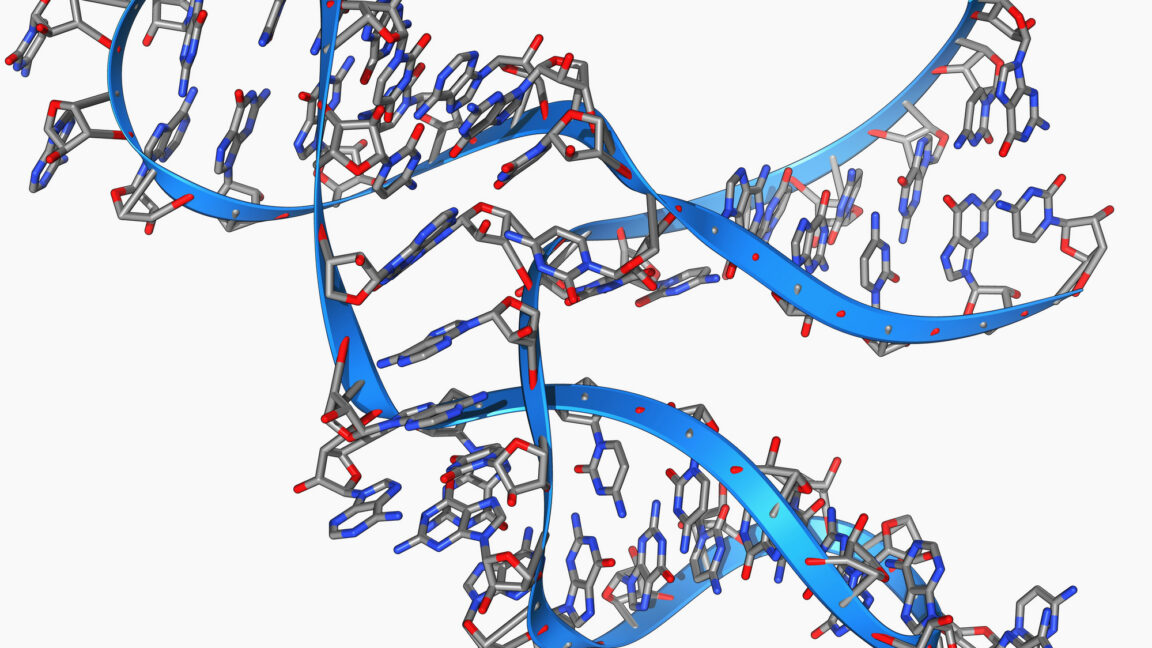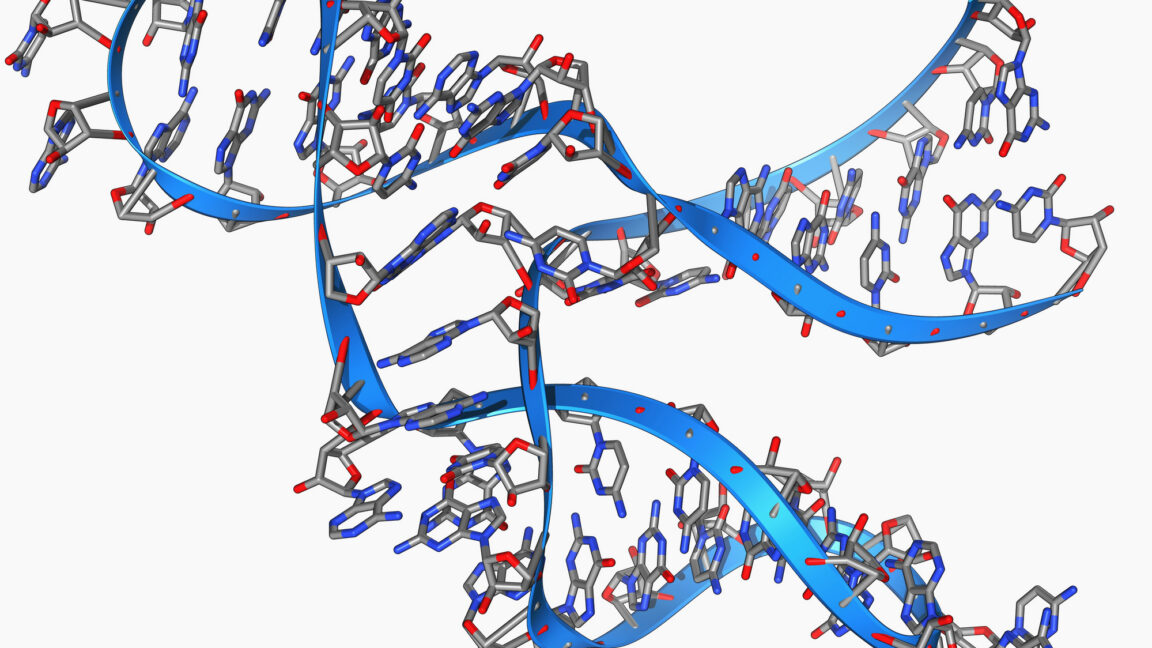
But the key finding was that it could synthesize a sequence that base-pairs with itself, and then synthesize itself by copying that sequence. This was horribly inefficient and took months, but it happened.
Throughout these experiments, the fidelity averaged about 95 percent, meaning that, in copying itself, it would make an average of two to three errors. While this means a fair number of its copies wouldn’t be functional, it also means the raw materials for an evolutionary selection for improved function—random mutations—would be present.
What this means
It’s worth taking a moment to consider the use of three-base RNA fragments by this enzyme. On the surface, this may seem a bit like cheating, since current RNA polymerases add sequence one base at a time. But in reality, any chemical environment that could spontaneously assemble an RNA molecule 45 bases long will produce many fragments shorter than that. So in many ways, this might be a more realistic model of the conditions in which life emerged.
The authors note that these shorter fragments may be essential for QT-45’s activity. The short ribozyme probably doesn’t have the ability to enzymatically pry base-paired strands of RNA apart to copy them. But in a mixture of lots of small fragments, there’s likely to be an equilibrium, with some base-paired sequences spontaneously popping open and temporarily base pairing with a shorter fragment. Working with these base-paired fragments is probably essential to the ribozyme’s overall activity.
Right now, QT-45 isn’t an impressive enzyme. But the researchers point out that it has only been through 18 rounds of selection, which isn’t much. The most efficient ribozyme polymerases we have at present have been worked on by multiple labs for years. I expect QT-45 to receive similar attention and improve significantly over time.
Also notable is that the team came up with three different ligases in a test of just a small subset of the possible total RNA population of this size. If that frequency holds, there are on the order of 1011 ligating ribozymes among the sequences of this size. Which raises the possibility that we could find far more if we do an exhaustive search. That suggests the first self-copying RNA might not be as improbable as it seems at first.
Science, 2026. DOI: 10.1126/science.adt2760 (About DOIs).
Source link